Deploying Landscapes on Codesphere
Learn how to deploy and run multiple services that can independently scale vertically and horizontally within a single workspace. Suitable for hosting entire application landscapes.
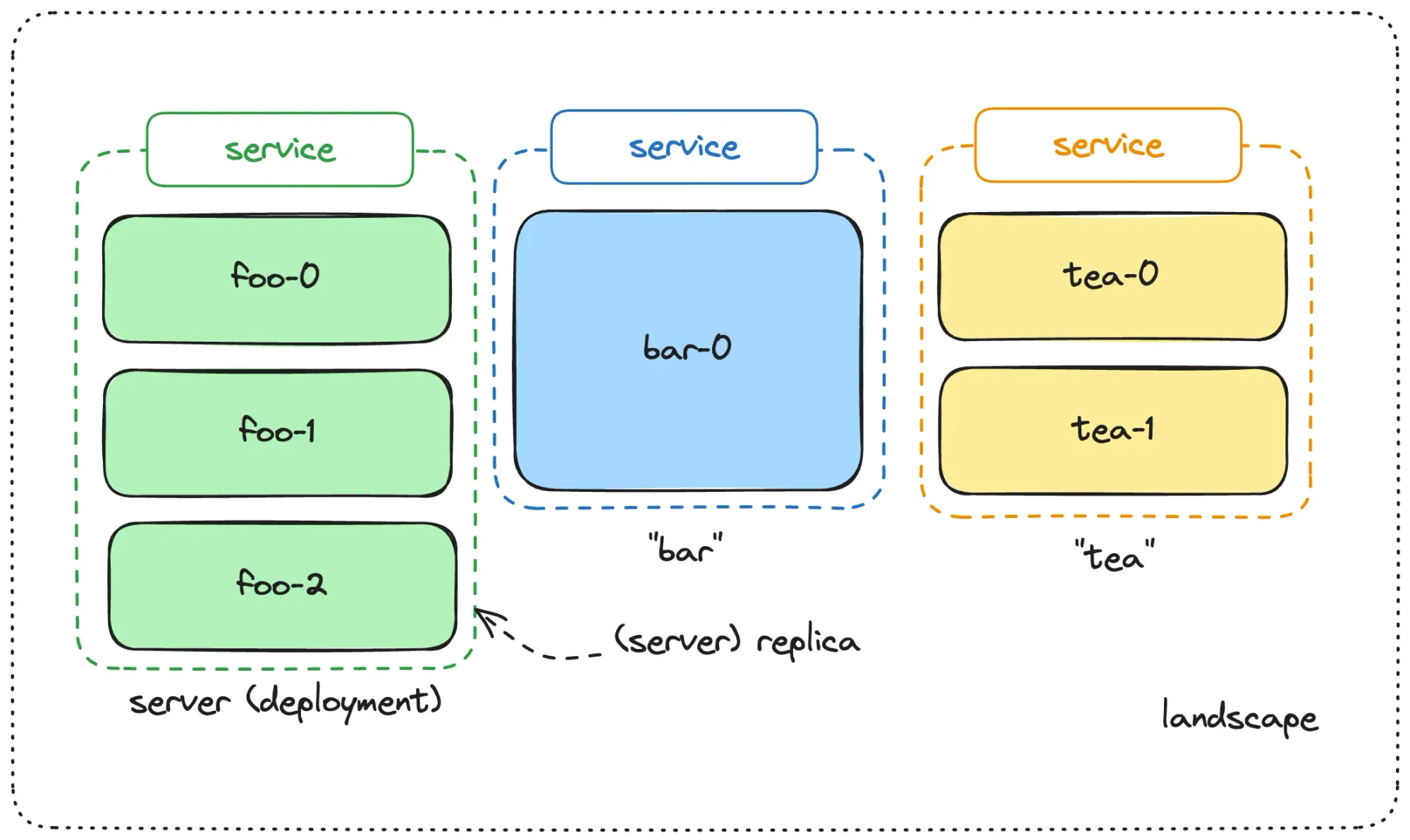
Deployments in Codesphere just received a major upgrade. You can now run multiple services that can independently scale vertically and horizontally within a single workspace.
With this you define your landscapes with all its services within your ci.yml file from the Codesphere UI. At the same time we are moving the entire Codesphere editor and filesystem operations into a separate deployment with individual resources. This separation will further improve the stability of your applications runtime execution and enable future improvements like vertical scaling for things like builds without interfering with your application.
Configuring multiple services
Services are defined in the Codesphere CI tab. You can create new or edit existing services by using the CI configuration editor.
For each service you need to choose a unique service name, the service's plan, a path from which the service serves traffic, the deployment mode (off-when-unused or always on) and the number of replicas. Once configured you add the commands to run the application of this service. For anyone already familiar with single service Codesphere workspaces you can think of it like having multiple run stages.
Similar to how our replicas work, all services run on the same shared file-system. This means only packages and build artefacts in the shared /home/user/app and /nix/store folder will be available within landscape services. The overall storage available to this workspace is defined by this workspaces IDE plan, and will later be freely configurable.
Paths are served from the perspective of a mono-repository by default, which means when defining a service with path /foo the application running there also needs to be serving traffic under this route so for example /foo/ would be the root from this application's perspective. Consequently all routes of the foo application need to include the prefix /foo/ so a valid example route would be /foo/yourRoute whereas /yourRoute would not be a valid route. We will be adding an option to strip that prefix from all routes for applications not originally designed with such a monorepo structure in mind in a future release.
Each service can be configured to have additional replicas for horizontal scaling capabilities. Combined these two features allow deploying and scaling large applications landscapes with numerous backend and or frontend services, databases and other managed services, for example you could run Codesphere inside of Codesphere.
Once you finish the configuration there are two options, you can either submit & deploy which will save the changes and update the landscape. Since this might include changes to your billing i.e. adding or upgrading service plans, a confirmation popup will show up and asks for your confirmation.
The run stage of all changed services will be restarted upon confirmation which can cause a short downtime, if you want to avoid that please follow the process described here: https://codesphere.com/articles/zero-downtime-releases
If you want to save your CI config changes without applying them directly you can also submit without syncing. In that case you will see a warning icon next to the run stage and a sync button to update the landscape to the currently configured state.
Exposing Multiple Ports (Advanced)
The Advanced Ports feature enables you to expose and manage multiple ports per service, providing greater flexibility to accommodate different applications and frameworks.
Supported Port Types
Currently, all ports exposed through this feature use TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). You can expose ports for various services, such as:
- HTTP/S: Commonly used for web servers, typically ports like 80, 443, or framework-specific defaults (3000, 8080).
- Generic TCP: Useful for databases and other services, such as PostgreSQL (5432) or Redis (6379).
Note: While you can expose additional ports, your main application or service should on port 3000.
Public vs. Internal Ports
Each port can be configured either as:
- Public (globe icon): Accessible externally via a unique subdomain in the format <workspace-id>-<port>-<service-name>.codesphere.com, as well as any connected custom domains.
- Internal (lock icon): Accessible exclusively within your private network domain (see details under private networking on this page).
Internal ports leverage Codesphere’s built-in private networking for secure internal communication. You can toggle between Public and Internal exposure by clicking on the port icon in the UI.
How to Configure Ports
Follow these steps to configure multiple ports:
- Open your landscape configuration.
- Activate the advanced settings for any given service.
- Specify the required port numbers.
- Choose the exposure type (Public or Internal) based on your use-case.
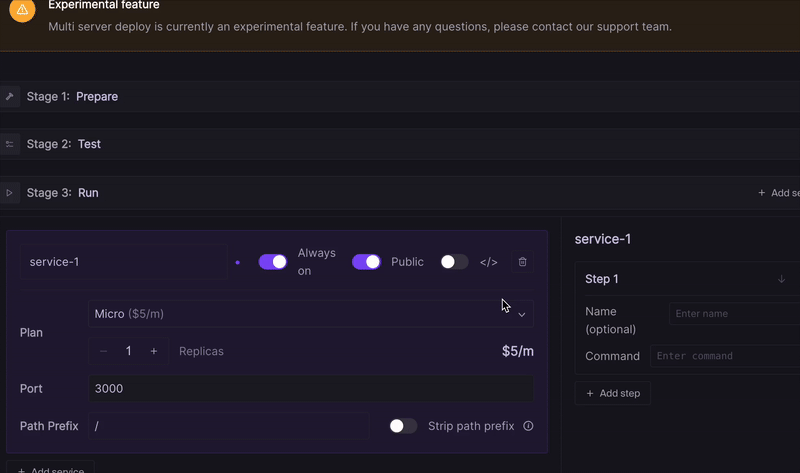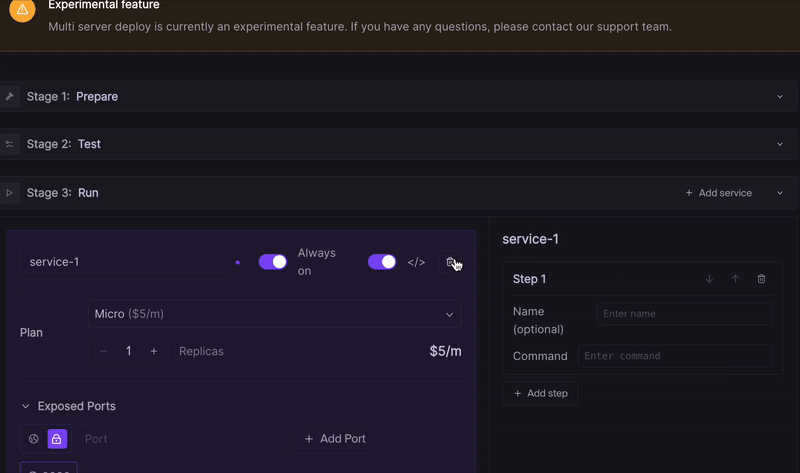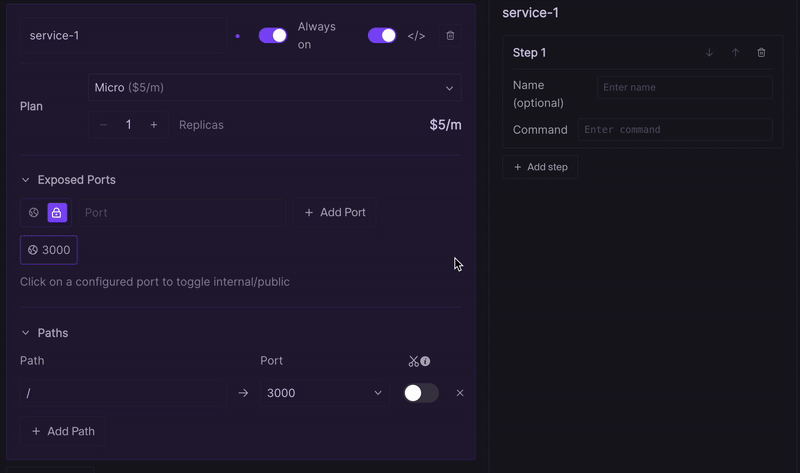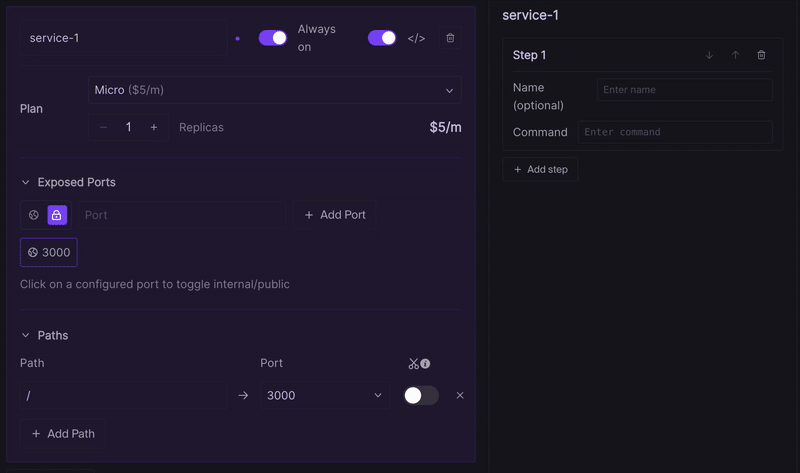
Path Mapping
Path mapping allows you to forward incoming requests from your workspace URL to specific ports of your services. In the basic network configuration, you can map only one path per server. The Advanced Ports feature allows multiple paths to be mapped to the same port, enabling flexible routing.
In this example:
- All routes belong to service-1.
- The root path / is exposed publicly on port 3000.
- The ports are not accessible via a subdomain, but can be reached through the paths /api and /admin-panel respectively.
- Path stripping is disabled for all paths
Example use cases
This section explains some examples where using the new multi service landscape deployment makes the most sense.
Separate frontend and backend
This is the most obvious and common case where having separate services that can scale independently is beneficial. Combine a lightweight frontend in your choice of tech stack with a more capable backend service in another stack.
Extending existing applications with additional (AI) services
You can now add self-hosted AI capabilities to any of your applications by deploying an additional backend service along your existing application. Services of a workspace can communicate with each other within the cluster i.e. without going through a public internet route first. This ensures low latency and efficient communication.
AI is not the only service that can be added this way. You can extend your applications capabilities with other backend services like a self hosted low code workflow tool i.e. n8n, a pdf server or an authentication service like keycloak just to name a few where we have one-click installable templates.
Private networking
Landscape deployments come with private networking capabilities out of the box. Services are able to communicate with each privately within the protected Codesphere network and you can select which service gets publicly exposed. This is great for building API gateway type of applications without worrying much about authentication.
To use private networking you need to configure your services to not call each other via their path but via their service name pattern i.e. http://ws-server-[WorkspaceId]-[serviceName]:3000. Note that this is a local http call and that this URL is only ever accessible for other services of the same landscape. It will not be accessible from the frontend nor the public internet. All services (both public and private services) can call each other this way but private services are exclusively accessible this way.
Implications of separating IDE and application resources
This section explains how the new landscape deployment differs from our previous single service workspaces and what to consider when working with a multi-service workspace for the first time.
All interactions happening in the Codesphere IDE are now running in a separate deployment. This deployment has its own resources. This has two major benefits: Firstly your interactions i.e. during releases, or debugging can never interfere with your production deployment service. Secondly this will allow much more flexible resource allocation for non-production workloads i.e. builds. We will be adding options to vertically scale the IDE resources up for a short time (i.e. during a build) and then down again.
In practice this means that your prepare and test stage are running on the IDE resources, so are your file tree interactions, all language servers resources and terminal interactions. If your IDE plan is too small for the workloads in your prepare stage for example you might experience OOM errors or unstable IDE navigation, but it can never interfere with your run stage execution.
Shared filesystem and avoiding concurrent writes
Just like our replicas all services will use the shared file system. The total available storage size is determined by the IDE plan and will later be separately configurable.
While less likely than with replicas you still need to ensure that your services don't concurrently write into the same file during runtime. If your services are structured in individual folders that typically will not be the case per default.
Shared storage is limited to the home/user/app/ directory and all subdirectories. If you install packages or set configurations in your prepare stage make sure that all of that is within the shared filesystem directory. Every change outside of this directory will not persist across restarts and will not be available to individual services at runtime.
Migrating from single service workspaces
We are rolling this out gradually (beginning with an opt in Beta) but eventually all new workspaces will be using the new landscape deployment mode per default. Use cases that only use a single service will then be a landscape deployment with a single service.
If you want to upgrade existing workspaces or repositories with an existing ci.yml you will be offered to update your CI config when opening the CI editor in the workspace. This will move your existing run stage into a first service. Please note currently this will create an additional plan that increases your monthly bill upon confirmation. We are working on a solution that will remedy this.
After completing the update you will need to commit the updated ci.yml to your repository otherwise you will be asked to upgrade again next time you create a workspace from the old configuration.
Alternatively you can check out this template repository which shows the separate backend / frontend use case: https://github.com/codesphere-cloud/landscape-twitter-clone.